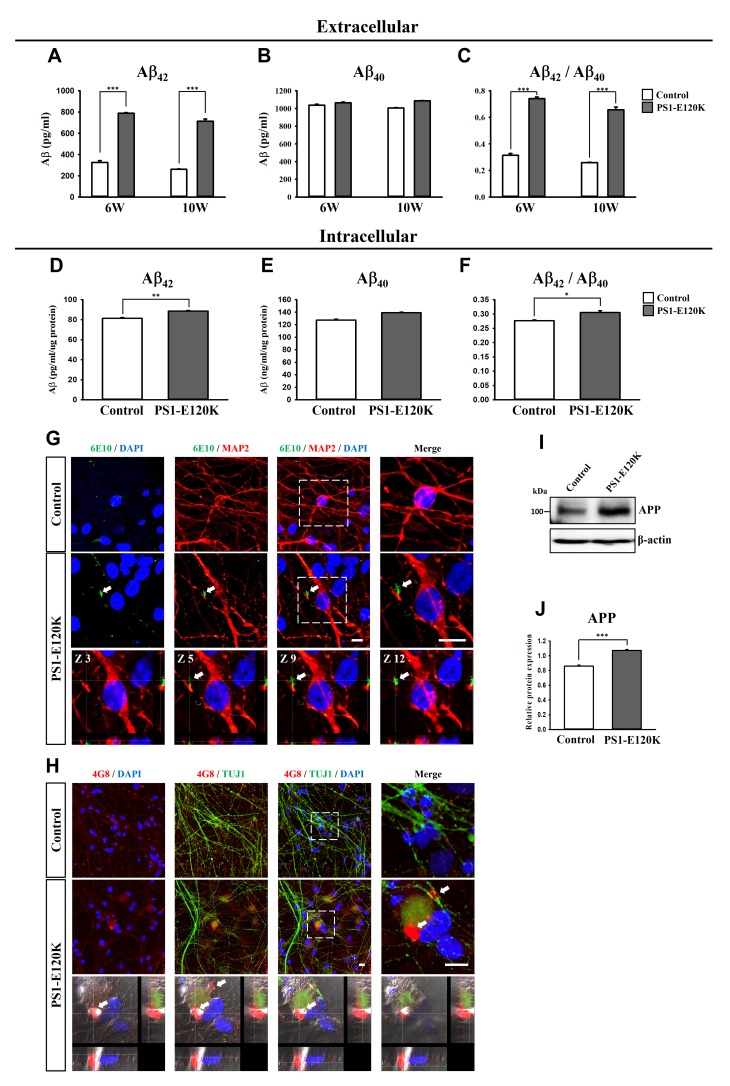
Fig. 4. Increase of Aβ deposits in the PS1-E120K iPSC-derived neurons, examined at 6 and 10 weeks after neuronal differentiation. ELISA detection of Aβ42 (A) and Aβ40 (B) secreted from the PS1-E120K iPSC-derived neurons into the medium (extracellular), which was measured at 48 hours after the last medium change. Levels of Aβ42 (A) and the ratio of Aβ42/Aβ40 (C) showed a dramatic increase in the PS1-E120K iPSC-derived neurons at both 6 and 10 weeks of neuronal differentiation. Intracellular Aβ42 (D) and Aβ40 (E) levels were measured in a total of 1 µg proteins from 10 week-differentiated neurons. Levels of the intracellular Aβ42 (D) and the ratio of Aβ42/Aβ40 (F) showed a significant increase in the PS1-E120K iPSC-derived neurons. (G, H) Detection of Aβ deposits using an antibody against 6E10 (shown in green) co-stained with MAP2 (red) (G) or using an antibody against 4G8 (shown in red) co-stained with and TUJ1 (green) (H) and DAPI (blue) at 10 weeks of neuronal differentiation. The bottom panels show the z-stack images of the 6E10 and 4G8-positive Aβ deposits (arrows) in the PS1-E120K iPSC-derived neurons. Scale bar: 10 µm. (I, J) Western blot analysis showing a significant increase of total APP expression levels in the PS1-E120K iPSC-derived neurons compared to the control. Representative ELISA, western blot and ICC images were obtained from three independent experiments.
© Exp Neurobiol


