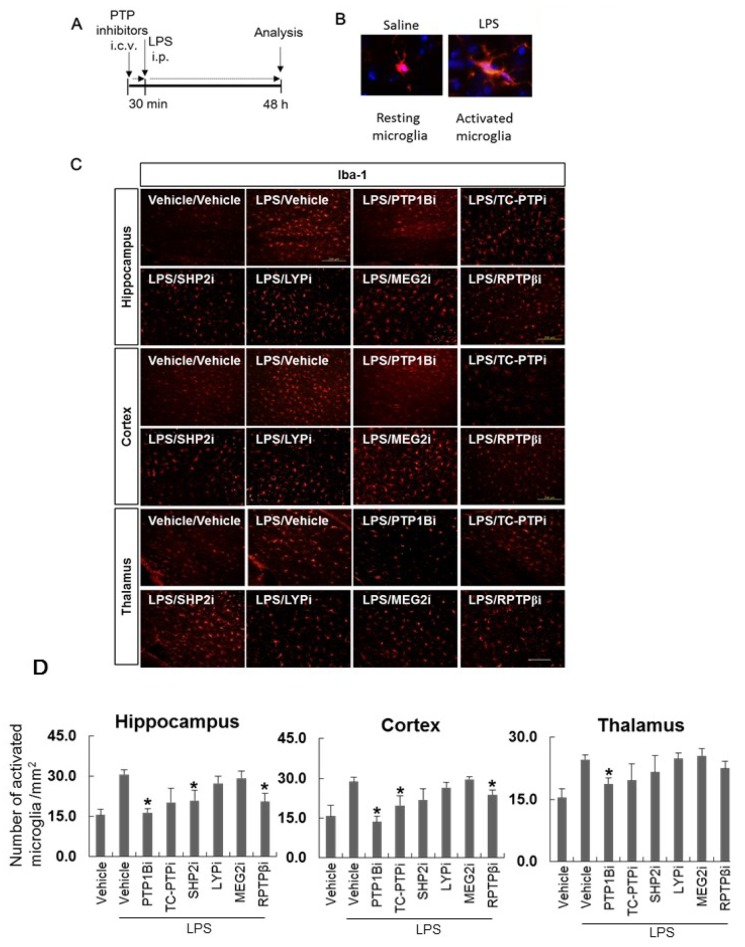
Fig. 4. PTP inhibitors suppress microglial activation in a mouse neuroinflammation model. (A) C57BL/6 mice were injected i.c.v. with vehicle (saline containing 0.5% DMSO and 5% propylene glycol) or PTP inhibitors (diluted in saline containing 5% propylene glycol). At 30 min after the injection of inhibitors for PTP1B, TC-PTP, SHP2, MEG2, LYP, and RPTPβ, mice were injected i.p. with LPS (5 mg/kg). The mice were anesthetized and transcardially perfused with ice-cold saline 48 h after the LPS injection. (B) Representative pictures of resting microglia and activated microglia stained with anti-Iba-1 antibody (a marker for microglia). (C) The brains were removed and the sections were stained with Iba-1 antibody. Iba-1-positive cells were observed in the mouse hippocampus, cortex, and thalamus. Inhibitors were indicated as PTP1Bi, TC-PTPi, SHP2i, MEG2i, LYPi, and RPTPβi. Scale bar, 200 µm. (D) The graph shows activated microglial cell number per mm2. *p<0.05 vs. LPS and vehicle. More than three brain sections were examined for each experimental group.
© Exp Neurobiol


