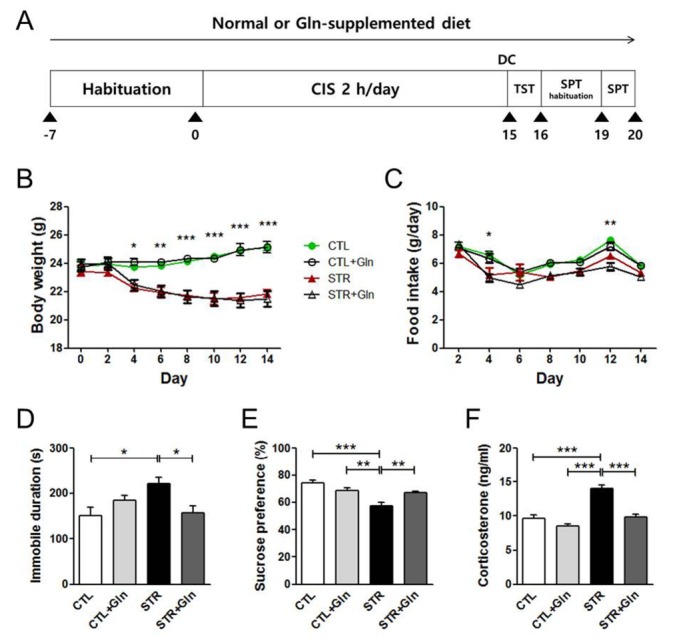
Fig. 1. Glutamine (Gln) supplementation inhibited the deleterious effects of chronic immobilization stress (CIS). (A) Experimental schedule. One batch was sacrificed by decapitation after CIS for molecular analysis, and the other was used for behavioral tests. Body weight (B) and food intake (C) were recorded every 2 days for 2 weeks from day 0. (D and E) The effects of CIS and Gln on immobility duration during the tail suspension test (D) and sucrose preference (E) were analyzed after CIS. (F) Plasma corticosterone levels were analyzed after CIS without behavioral tests. The bars represent the means± SEMs. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 in the two-way (B and C) or one-way (D~F) analysis of variance test with Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test (n=5~7).
© Exp Neurobiol