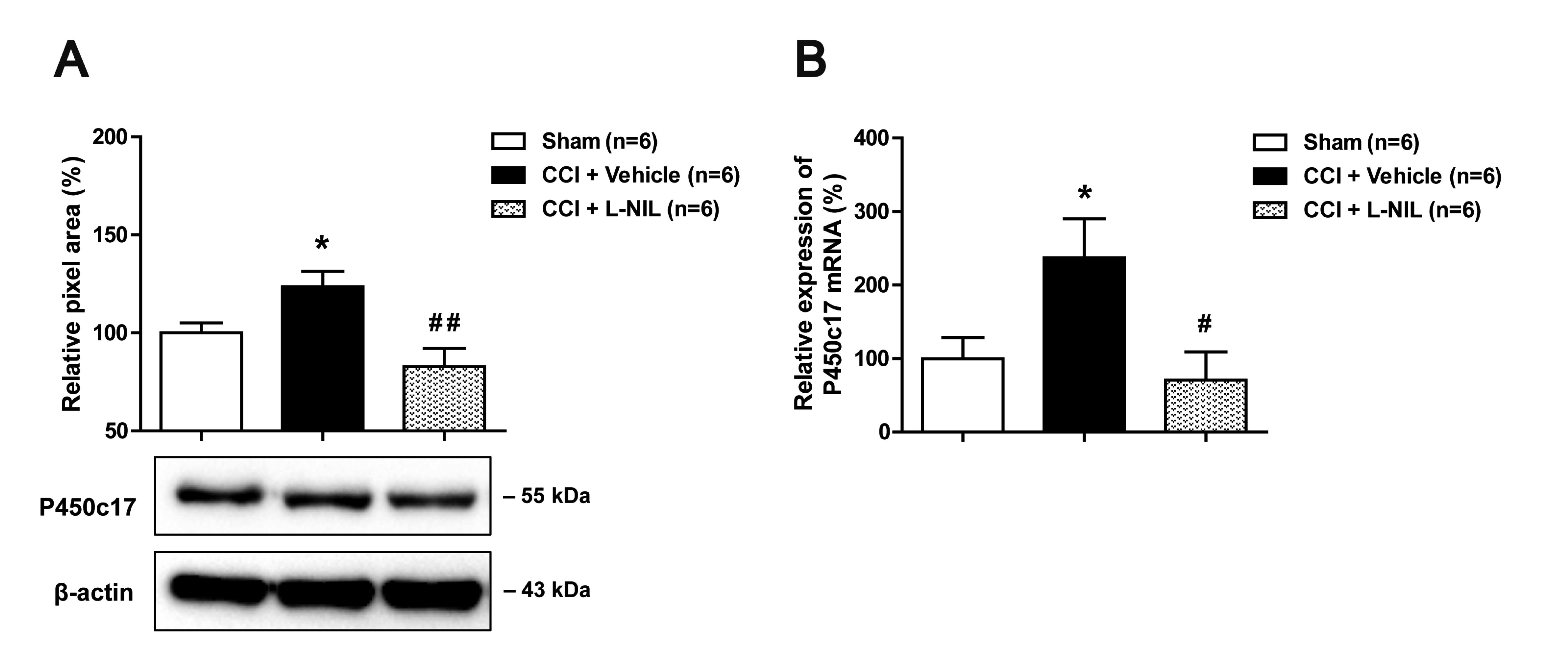
Fig. 4. Graphs illustrating the effect of i.t. administration of the NOS-II inhibitor, L-NIL on the protein and mRNA levels of P450c17 in the lumbar spinal cord dorsal horn of CCI rats. (A) Results of Western blot analysis showed that the CCI-induced increase in the protein level of cytochrome P450c17 in the spinal cord was suppressed by intrathecal (i.t.) administration of L-NIL (60 nmol). n=6 rats/group. (B) The CCI-induced increase in the level of P450c17 mRNA in the spinal cord was also suppressed by i.t. administration of L-NIL (60 nmol). n=6 rats/group. Drug or vehicle was administrated twice a day from days 0 to 5 post-surgery. The spinal cord dorsal horn was sampled at 5 days after surgery. *p<0.05 vs. Sham; #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 vs. vehicle-treated group. A and B, one-way ANOVA followed by a Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test for post-hoc analysis.
© Exp Neurobiol