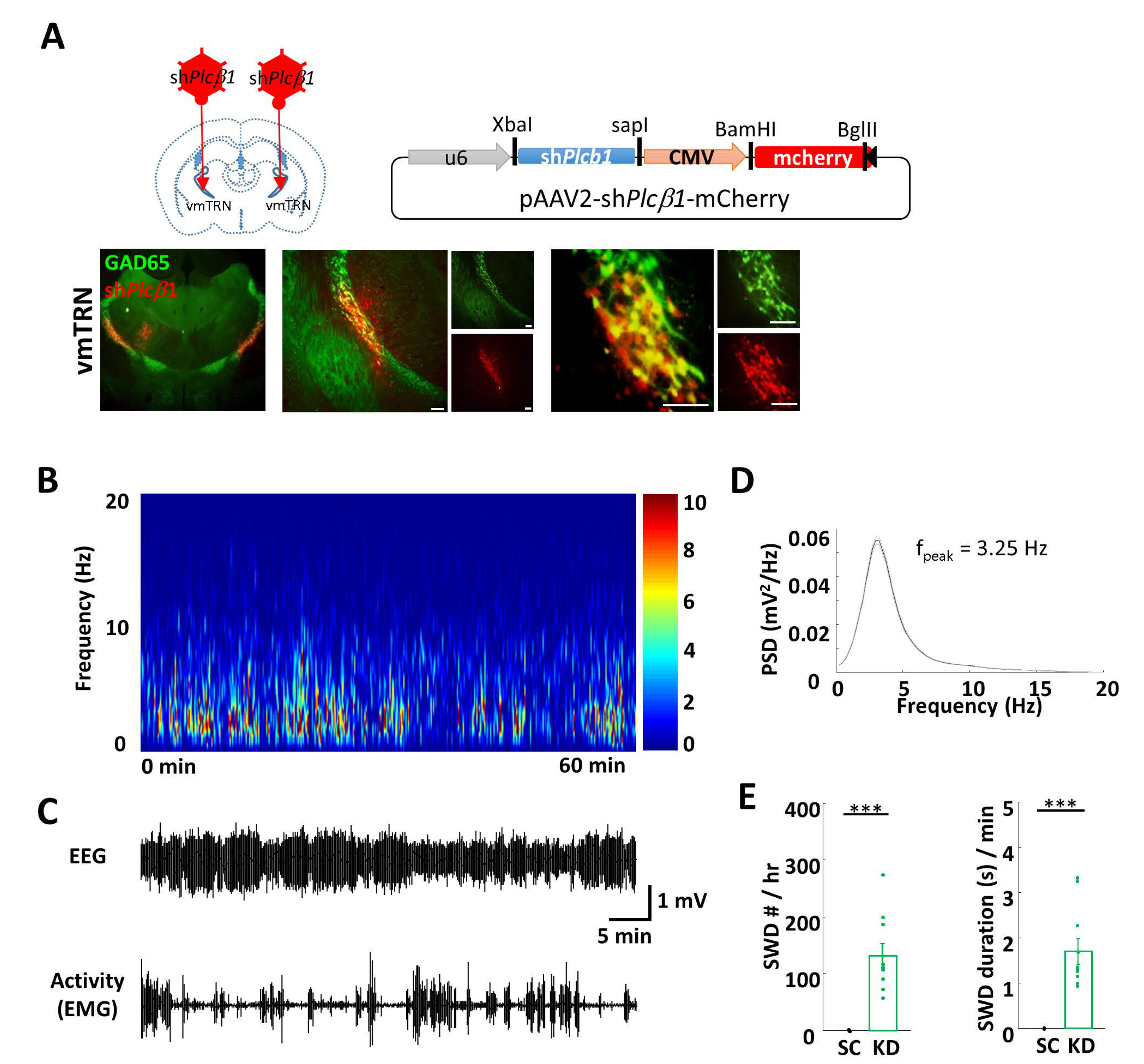
Fig. 3. Selective knockdown (KD) of Plcβ1 in the vmTRN induces absence seizures. (A) Scheme of selective KD of Plcβ1 in the vmTRN. Left, vmTRN injection site (AP -1.1, ML ±1.8, DV -3.0). Right, schematic representation of the targeting vector for KD virus. Bottom, microinjection of the AAV-shPlcβ1-mCherry virus into the vmTRNs of GAD65GFP transgenic mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Average EEG power spectrograms of Plcβ1+/- and Plcβ1 KD mice. (C) Representative EEG and EMG traces from Plcβ1 KD mice. (D) Power analysis of spontaneous SWDs. Plcβ1 KD mice showed a peak frequency at 3.25 Hz. (E) Summary graphs of the total numbers (left) and average durations (right) of SWDs in scrambled (n=9), and Plcβ1 KD (n=13) mice. The values in the KD group was significantly different from in the SC group. The data are presented as the mean±SEM, one-way ANOVA, ***p<0.001, post hoc (Bonferroni).
© Exp Neurobiol