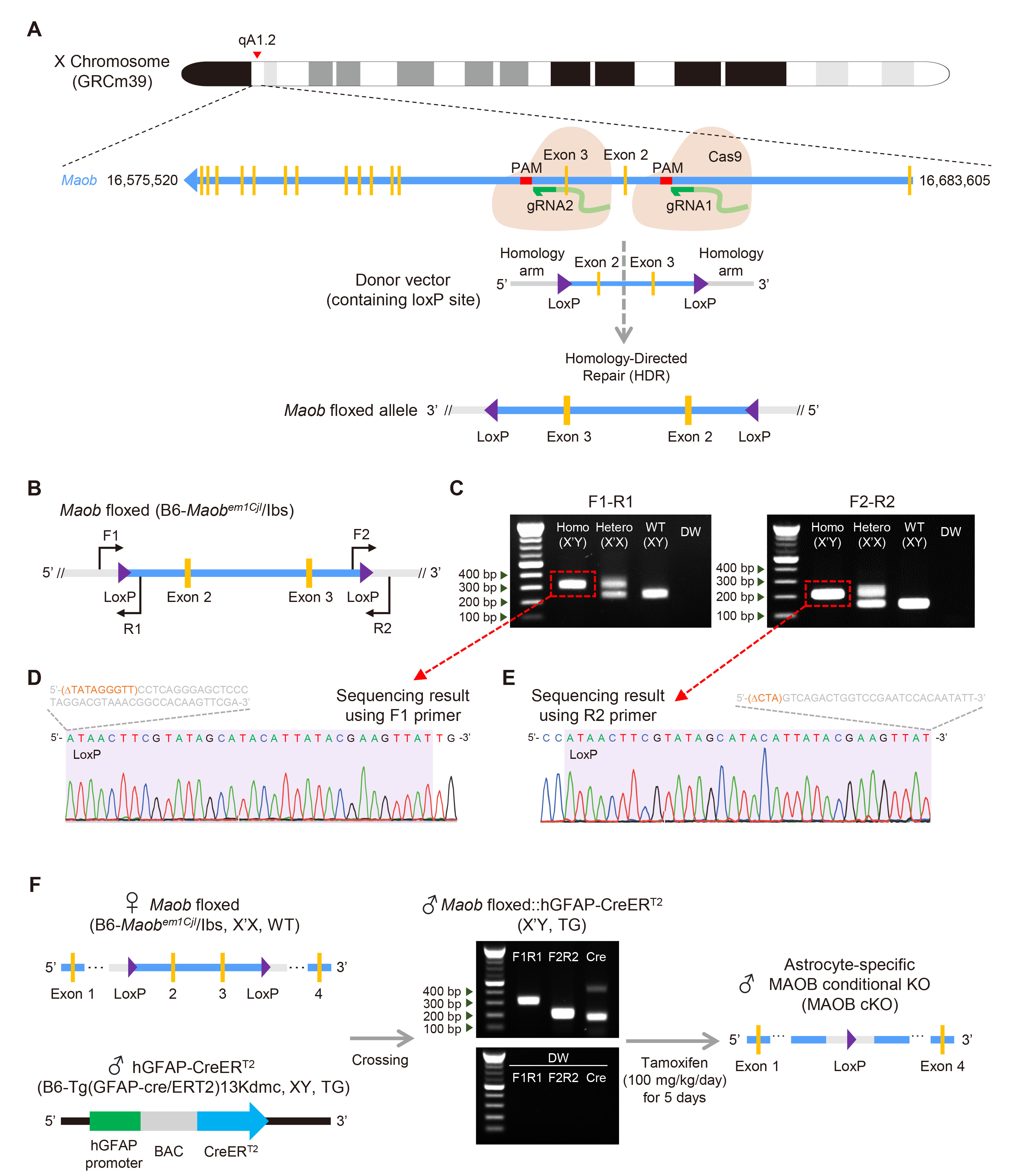
Fig. 1. Generation of Maob floxed and astrocyte-specific MAOB cKO mouse lines. (A) Schematic diagram of Maob location on mouse X chromosome (top) and construction of Maob floxed allele using the CRIPSR-Cas9 technique (bottom). (B) Construct of Maob floxed allele in Maob floxed mouse (B6-Maobem1Cjl/Ibs) with primer sets for genotyping (F1-R1, F2-R2) and sequencing (F1, R2) for each loxP site. (C) Genotyping result of homozygote, heterozygote, WT, and distilled water (DW) as no template control using F1-R1 primer (left) and F2-R2 primer (right). Red dotted boxes and lines indicate extracted DNA bands for sequencing in (D) and (E). (D) Sequencing result of loxP site in upstream of exon 2 using F1 primer. Orange and grey sequences indicate deleted and inserted intronic sequences from the original Maob, respectively. (E) Sequencing result of loxP site in downstream of exon 2 using R2 primer. Orange and grey sequences indicate deleted and inserted intronic sequences from the original Maob, respectively. (F) Schematic diagram showing generation of astrocyte-specific MAOB cKO mice by crossing Maob floxed mice (B6-Maobem1Cjl/Ibs, X’X, WT) with hGFAP-CreERT2 (B6-Tg(GFAP-cre/ERT2)13Kdmc, XY, TG) (left), and genotyping results of Maob floxed::hGFAP-CreERT2 (X’Y, TG) with F1-R1, F2-R2, and two pairs of primers for hGFAP-CreERT2 with no template control of each primer set (middle), and construct of Maob allele in astrocyte-specific MAOB cKO mouse (right).
© Exp Neurobiol


