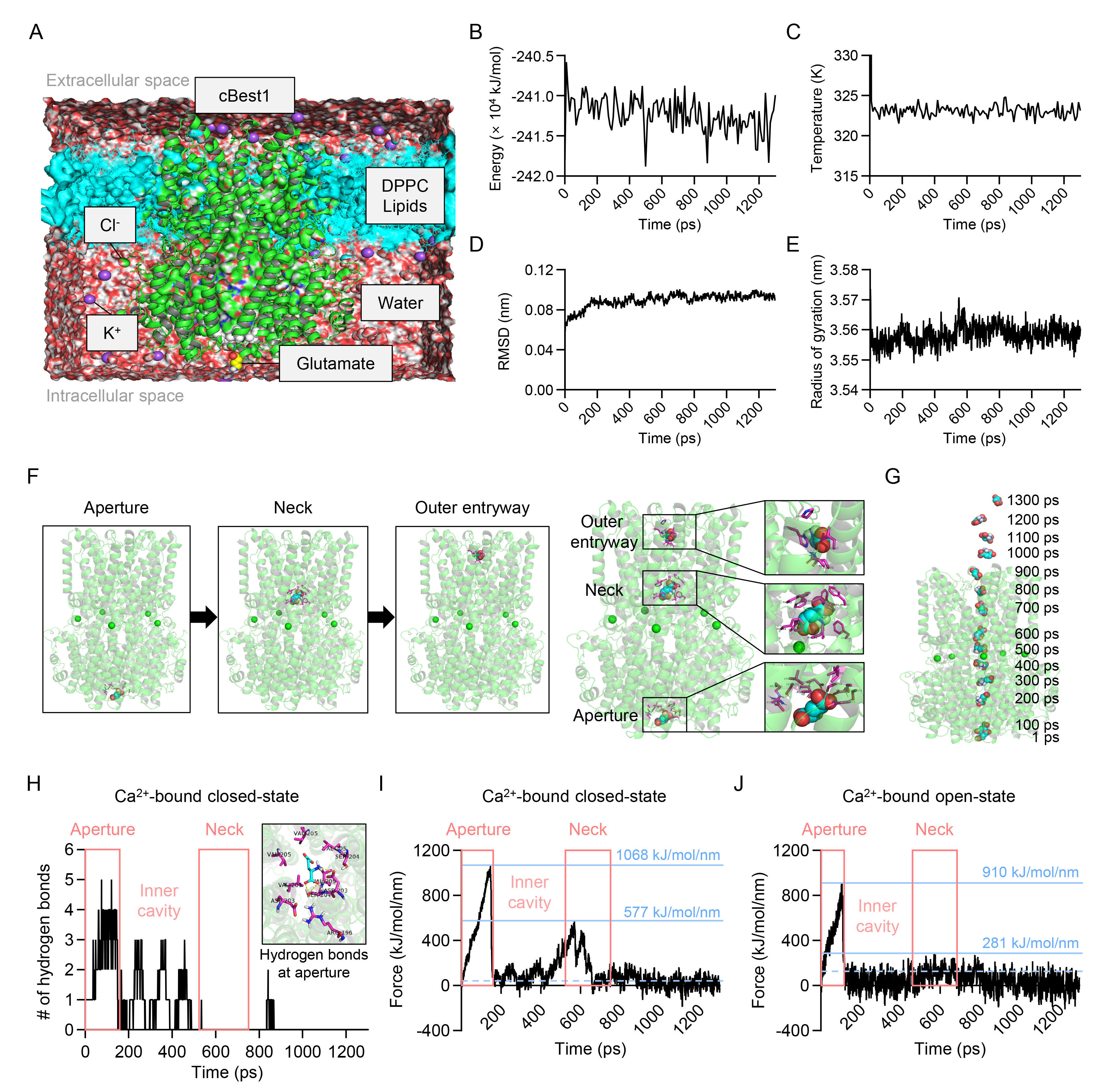
Fig. 2. Glutamate permeates through the ion-conducting pore of cBest1. (A) Representative molecular dynamics simulation system with glutamate and cBest1 model structure with amino acids 1-405 at the membrane. cBest1, green structure; glutamate, sphere model; DPPC lipids, cyan model; water, transparent red and white sphere; K+, purple sphere; Cl-, green sphere; V205 residue, white sphere. (B~E) Molecular dynamics simulation analysis during umbrella sampling simulation for the potential energy (B), temperature (C), RMSD (D), and radius of gyration (E) as a function of umbrella sampling simulation time (0~1300 ps). (F) Left, representative snapshots showing the relative position of glutamate at the aperture, neck, and outer entryway during umbrella sampling simulation. Right, the positions of glutamate at the aperture, neck, and outer entryway with the magnified images showing interaction between glutamate and residues in each region. The cBest1 is depicted as a Ca2+-bound (green sphere) structure (transparent green ribbon diagram). Glutamate and surrounding residues are represented by the sphere model (carbon, cyan; oxygen, red; nitrogen, blue; hydrogen, white) and the stick model, respectively. (G) The detailed positions of glutamate at every 100 ps projected on the 1 ps cBest1 structure during umbrella sampling simulation. (H) The number of hydrogen bonds as a function of umbrella sampling simulation time in Ca2+-bound closed-state cBest1 model structure with amino acids 1-405. Inset, the hydrogen bond interactions (yellow dotted lines) between glutamate and cBest1 residues at the aperture region at 100 ps of umbrella sampling simulation. Glutamate and surrounding residues are represented by the stick model. (I, J) The external pulling force as a function of umbrella sampling simulation time in Ca2+-bound closed-state (I; amino acids 1-405) and Ca2+-bound open-state cBest1 model structure (J; amino acids 1-345). Blue dotted lines indicate the external pulling force value in the Ca2+-bound closed-state (I; 42 kJ/mol/nm, averaged over 659~750 ps) and in the Ca2+-bound open-state (J; 122 kJ/mol/nm, averaged over 592~683 ps).
© Exp Neurobiol


