Articles
Article Tools
Stats or Metrics
Article
Review Article
Exp Neurobiol 2020; 29(5): 325-333
Published online October 31, 2020
https://doi.org/10.5607/en20042
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
Urinary Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Wongi Seol1*, Hyejung Kim1 and Ilhong Son1,2*
1InAm Neuroscience Research Center, 2Department of Neurology, Sanbon Medical Center, College of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Gunpo 15865, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Ilhong Son, TEL: 82-31-390-2486, FAX: 82-31-390-2414
e-mail: sonih@wku.ac.kr
Wongi Seol, TEL: 82-31-390-2411, FAX: 82-31-390-2414
e-mail: wseolha@gmail.com
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
Global incidence of neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) is rapidly increasing, but the diagnosis of these diseases at their early stage is challenging. Therefore, the availability of reproducible and reliable biomarkers to diagnose such diseases is more critical than ever. In addition, biomarkers could be used not only to diagnose diseases but also to monitor the development of disease therapeutics. Urine is an excellent biofluid that can be utilized as a source of biomarker to diagnose not only several renal diseases but also other diseases because of its abundance in invasive sampling. However, urine was conventionally regarded as inappropriate as a source of biomarker for neurodegenerative diseases because it is anatomically distant from the central nervous system (CNS), a major pathologic site of NDD, in comparison to other biofluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma. However, recent studies have suggested that urine could be utilized as a source of NDD biomarker if an appropriate marker is predetermined by metabolomic and proteomic approaches in urine and other samples. In this review, we summarize such studies related to NDD.
Graphical Abstract
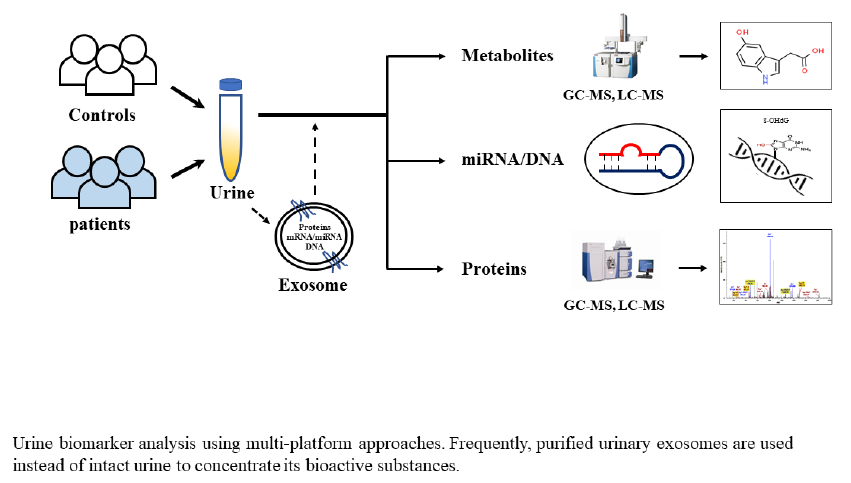
Keywords: Urine, Biomarkers, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease


