Articles
Article Tools
Stats or Metrics
Article
Original Article
Exp Neurobiol 2018; 27(2): 129-138
Published online April 30, 2018
https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2018.27.2.129
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
Black Rice (Oryza sativa L ., Poaceae) Extract Reduces Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Death Induced by Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Mice
Sun-Nyoung Hwang1†, Jae-Cheon Kim1†, Mohammad Iqbal Hossain Bhuiyan1,Joo Youn Kim1, Ji Seon Yang2, Shin Hee Yoon2, Kee Dong Yoon3 and Seong Yun Kim1*
Departments of 1Pharmacology and 2Physiology, Catholic Neuroscience Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, 3College of Pharmacy, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon 14662, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
TEL: 82-2-2258-7324, FAX: 82-2-536-2485
e-mail: syk@catholic.ac.kr
†These authors contributed equally
Abstract
Rice is the most commonly consumed grain in the world. Black rice has been suggested to contain various bioactive compounds including anthocyanin antioxidants. There is currently little information about the nutritional benefits of black rice on brain pathology. Here, we investigated the effects of black rice (
Graphical Abstract
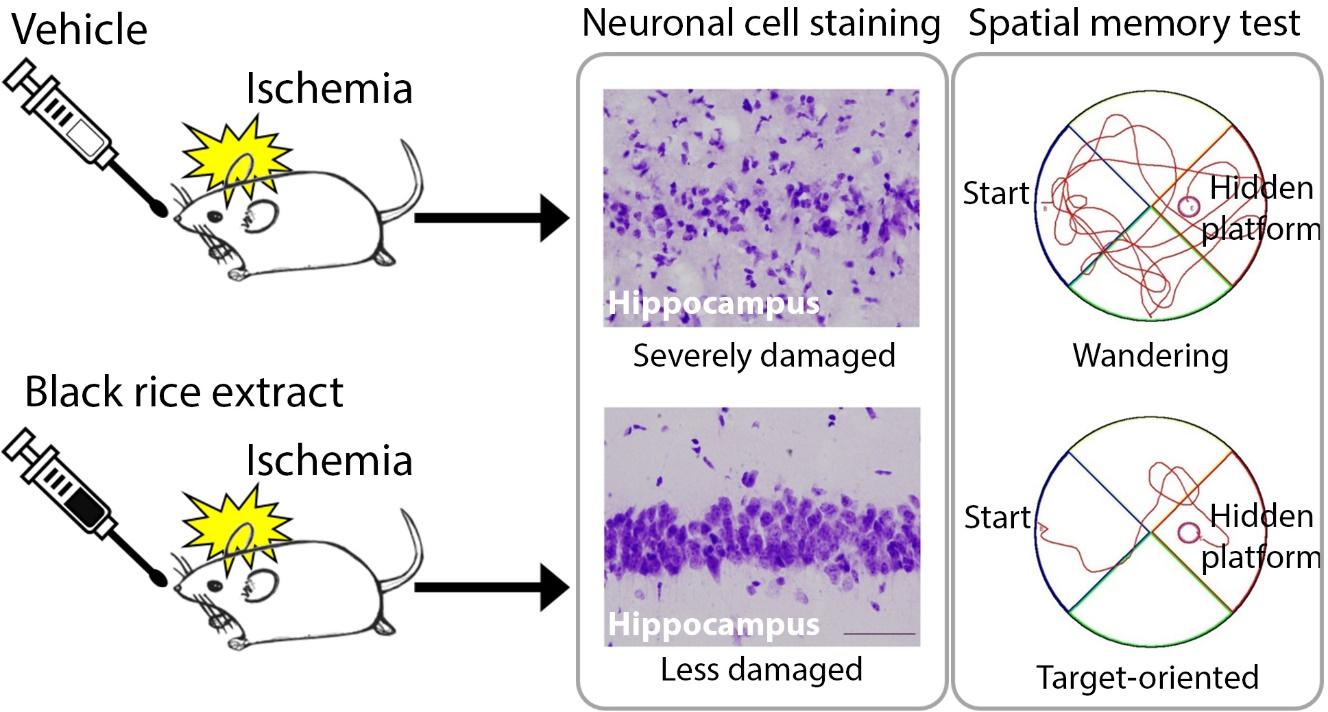
Keywords: Oryza sativa, brain ischemia, neuroprotection, hippocampus, memory and learning tests


