Articles
Article Tools
Stats or Metrics
Article
Original Article
Exp Neurobiol 2020; 29(4): 285-299
Published online August 31, 2020
https://doi.org/10.5607/en20025
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
Synchrony of Spontaneous Burst Firing between Retinal Ganglion Cells Across Species
Jungryul Ahn1, Huu Lam Phan2, Seongkwang Cha1, Kyo-in Koo2, Yongseok Yoo3* and Yong Sook Goo1*
1Department of Physiology, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju 28644,
2Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 44610,
3Department of Electronics Engineering, Incheon National University, Incheon 22012, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Yongseok Yoo, TEL: 82-32-835-8453, FAX: 82-32-835-0774
e-mail: yyoo@inu.ac.kr
Yong Sook Goo, TEL: 82-43-261-2870, FAX: 82-43-272-1603
e-mail: ysgoo@chungbuk.ac.kr
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and
reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
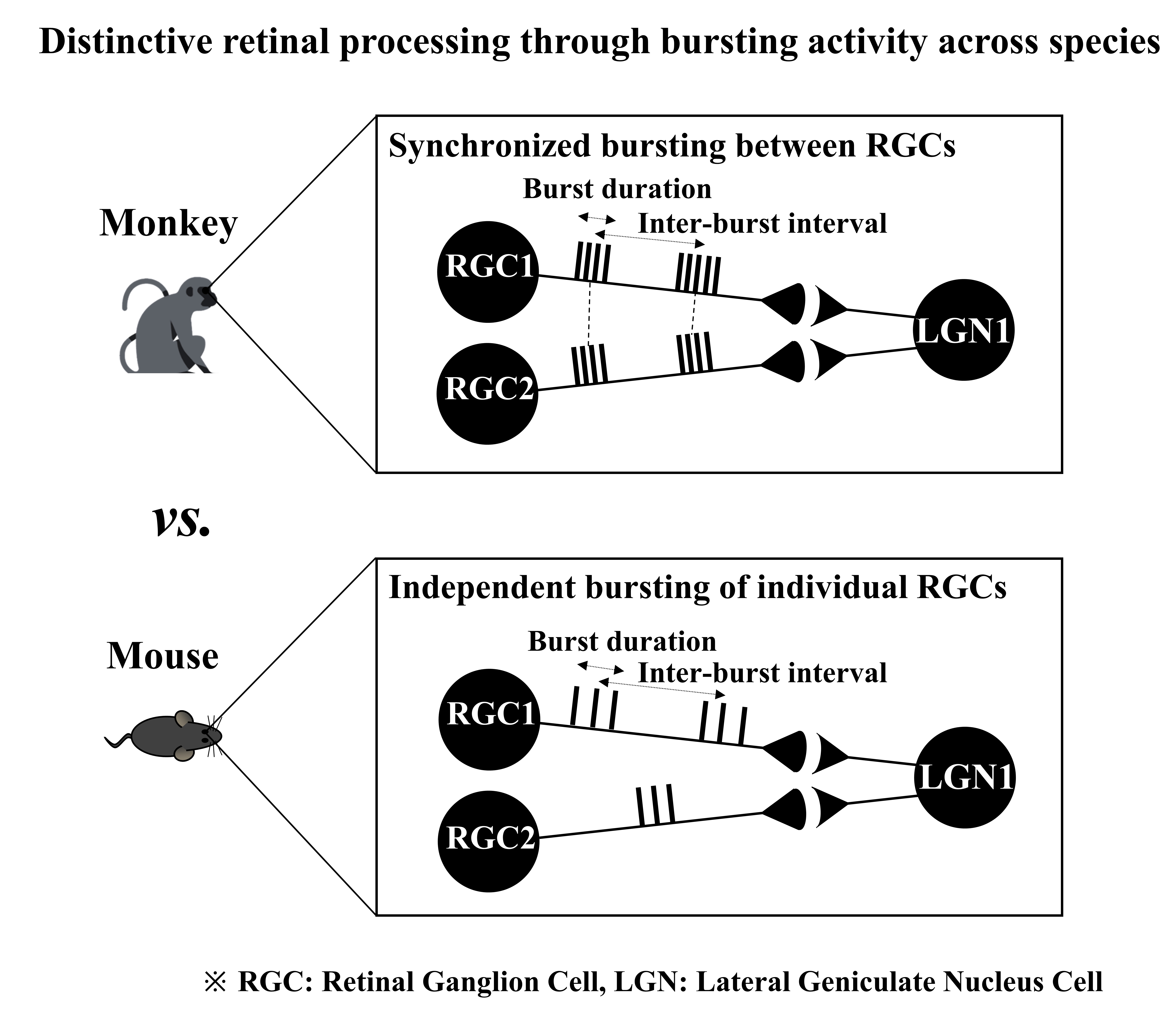
Neurons communicate with other neurons in response to environmental changes. Their goal is to transmit information to their targets reliably. A burst, which consists of multiple spikes within a short time interval, plays an essential role in enhancing the reliability of information transmission through synapses. In the visual system, retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), the output neurons of the retina, show bursting activity and transmit retinal information to the lateral geniculate neuron of the thalamus. In this study, to extend our interest to the population level, the burstings of multiple RGCs were simultaneously recorded using a multi-channel recording system. As the first step in network analysis, we focused on investigating the pairwise burst correlation between two RGCs. Furthermore, to assess if the population bursting is preserved across species, we compared the synchronized bursting of RGCs between marmoset monkey (callithrix jacchus), one species of the new world monkeys and mouse (C57BL/6J strain). First, monkey RGCs showed a larger number of spikes within a burst, while the inter-spike interval, burst duration, and inter-burst interval were smaller compared with mouse RGCs. Monkey RGCs showed a strong burst synchronization between RGCs, whereas mouse RGCs showed no correlated burst firing. Monkey RGC pairs showed significantly higher burst synchrony and mutual information than mouse RGC pairs did. Comprehensively, through this study, we emphasize that two species have a different bursting activity of RGCs and different burst synchronization suggesting two species have distinctive retinal processing.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords: Information transmission, Burst correlation, Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), Primate retina, Burst analysis


