Articles
Article Tools
Stats or Metrics
Article
Original Article
Exp Neurobiol 2022; 31(3): 196-207
Published online June 30, 2022
https://doi.org/10.5607/en22019
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
The Change in Circadian Rhythms in P301S Transgenic Mice is Linked to Variability in Hsp70-related Tau Disaggregation
Song Mi Han1,2, Yu Jung Jang1,2, Eun Young Kim2,3 and Sun Ah Park1,2,4*
1Lab for Neurodegenerative Dementia, Department of Anatomy, Ajou University School of Medicine, 2Neuroscience Graduate Program, Department of Biomedical Sciences, Ajou University Graduate School of Medicine, 3Department of Brain Science, Ajou University School of Medicine, 4Department of Neurology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon 16499, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
TEL: 82-31-219-5030, FAX: 82-31-219-5039
e-mail: sap001@ajou.ac.kr
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
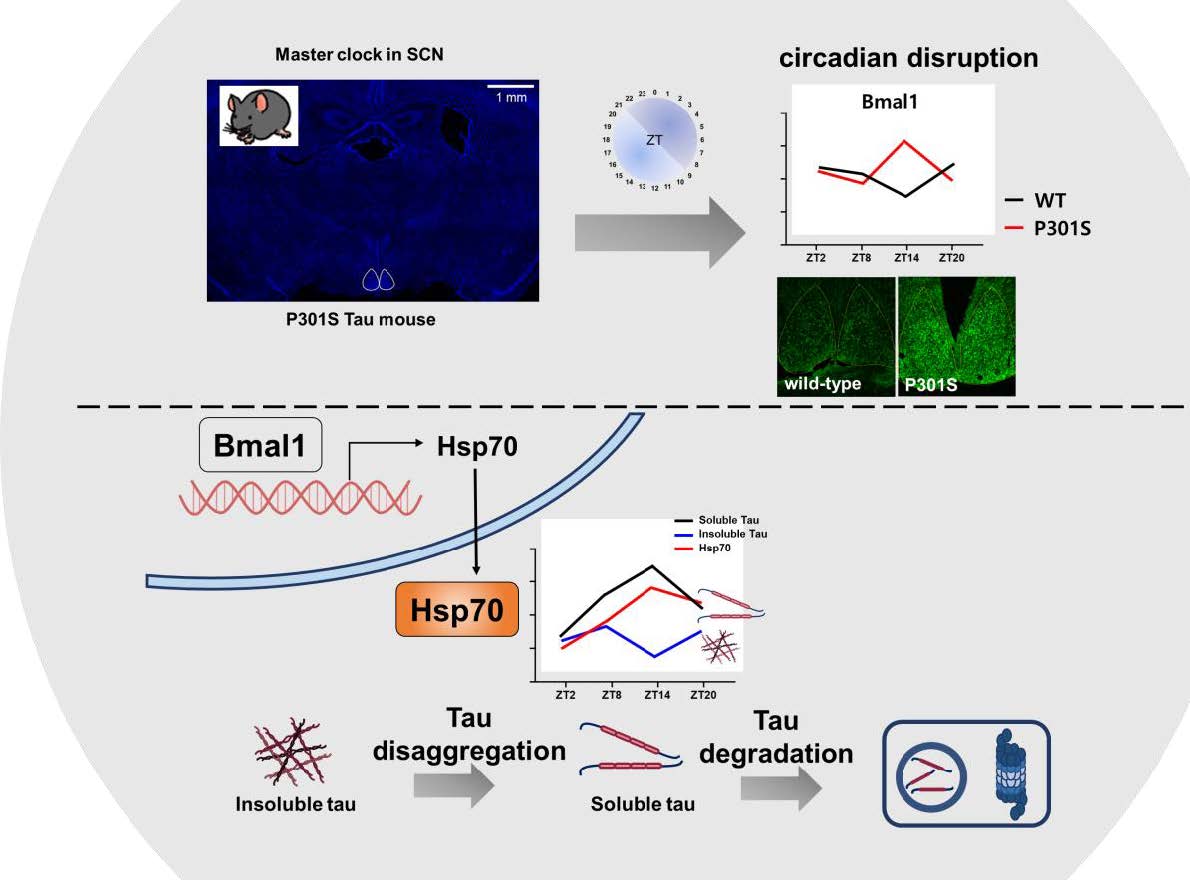
Circadian disruption often involves a neurodegenerative disorder, such as Alzheimer’s disease or frontotemporal dementia, which are characterized by intraneuronal tau accumulations. The altered sleep pattern and diurnal rhythms in these disorders are the results of tau pathology. The circadian disturbance in reverse is thought to develop and potentially aggravate the condition. However, the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. In this study, perturbed oscillations in BMAL1 , the core clock gene, were observed in P301S tau transgenic mice. Tau fractionation analysis of the hippocampus revealed profound fluctuations in soluble and insoluble tau protein levels that were in opposite directions to each other according to zeitgeber time. Interestingly, a diurnal oscillation was detected in the heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (Hsp70) chaperone that was in-phase with soluble tau but out-of-phase with insoluble tau. Tau protein levels decreased in the soluble and insoluble fractions when Hsp70 was overexpressed in HEK293T cells. Transfection of the BMAL1 carrying vector was continual with the increase in Hsp70 expression and diminished tau protein levels, and it was effectively attenuated by the knockdown of Hsp70, suggesting that Bmal1 could modulate tau protein by Hsp70. Our results suggest that altered circadian oscillations affect tau status and solubility by modulating Hsp70 expression in an experimental model of tau pathology. These findings suggest Hsp70 as a possible pathogenic link between circadian disruption and aggravations of tau pathology.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords: Tauopathies, Tau protein, Hsp70 heat-shock proteins, Circadian rhythm


