Articles
Article Tools
Stats or Metrics
Article
Original Article
Exp Neurobiol 2023; 32(1): 42-55
Published online February 28, 2023
https://doi.org/10.5607/en22044
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
Reelin and APP Cooperatively Modulate Dendritic Spine Formation In Vitro and In Vivo
Hyun-ju Lee1*, Jin-Hee Park1,2, Justin H. Trotter3, James N. Maher4, Kathleen E. Keenoy4, You Mi Jang1, Youngeun Lee5, Jae-Ick Kim5, Edwin J. Weeber3 and Hyang-Sook Hoe1,2,4*
1Department of Neural Development and Disease, Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI), Daegu 41062, 2Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology (DGIST), Daegu 42988, Korea, 3Department of Molecular Pharmacology and Physiology, USF Health Byrd Alzheimer’s Institute, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL 33613, 4Department of Neuroscience, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC 20057, USA, 5Department of Biological Sciences, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), Ulsan 44919, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Hyang-Sook Hoe, TEL: 82-53-980-8310, FAX: 82-53-980-8309
e-mail: sookhoe72@kbri.re.kr
Hyun-ju Lee, TEL: 82-53-980-8313, FAX: 82-53-980-8309
e-mail: hjlee@kbri.re.kr
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but the normal function of APP at synapses is poorly understood. We and others have found that APP interacts with Reelin and that each protein is individually important for dendritic spine formation, which is associated with learning and memory,
Graphical Abstract
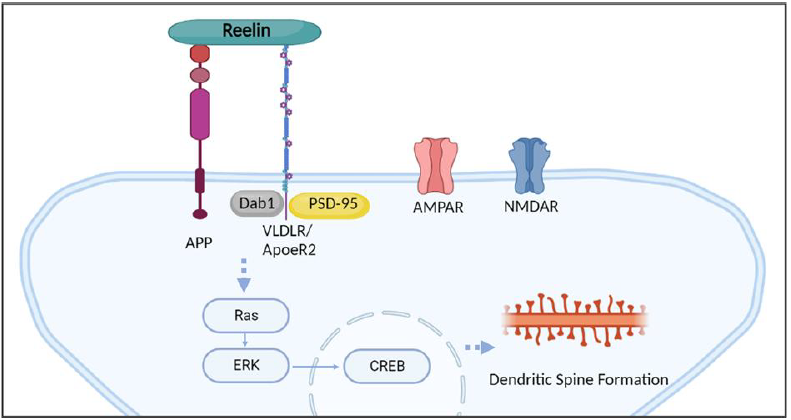
Keywords: APP, Reelin, Dendritic spine, Alzheimer’s disease, Ras signaling


