Articles
Article Tools
Stats or Metrics
Article
Review Article
Exp Neurobiol 2023; 32(2): 57-67
Published online April 30, 2023
https://doi.org/10.5607/en23010
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
Impaired Cholesterol Metabolism, Neurons, and Neuropsychiatric Disorders
So Yeong Cheon1,2*
1Department of Biotechnology, College of Biomedical & Health Science, Konkuk University, Chungju 27478,
2Research Institute for Biomedical & Health Science, Konkuk University, Chungju 27478, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
TEL: 82-43-840-3616
e-mail: sycheon14@kku.ac.kr
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
Cholesterol metabolism plays an essential role in cellular functions (including as a component of the plasma membrane, as an energy source, and in hormone production) under normal conditions. Dysregulated cholesterol metabolism causes a wide spectrum of pathological conditions, leading to neuropsychiatric disorders, such as anxiety and depression. In addition, patients with neuropsychiatric disorders also have impaired cholesterol metabolism. Therefore, metabolic disturbances are closely associated with the neuropsychiatric disorders. Although immune disturbance, neuroinflammation, a dysregulated neurotransmitter system, and oxidative stress have been suggested as pathophysiology of neuropsychiatric disorders, dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism is also found in patients with psychiatric diseases. As expected, patients with mental illness appear to be at risk of metabolic disorders, including metabolic syndrome, in which cholesterol influences altered neuronal homeostasis, such as neuronal cell toxicity, neuronal cell death, and neuronal structures and functions, including synaptogenesis, neurogenesis, axonogenesis, and action potential. Therefore, reversing impaired or abnormal cholesterol metabolism may help restore neuronal injury found in mental illness. This review is aimed to discuss the links between cholesterol metabolism impairment and neuropsychiatric disorders and provides insights into neuronal dysfunction due to abnormal cholesterol metabolism in neuropsychiatric disorders.
Graphical Abstract
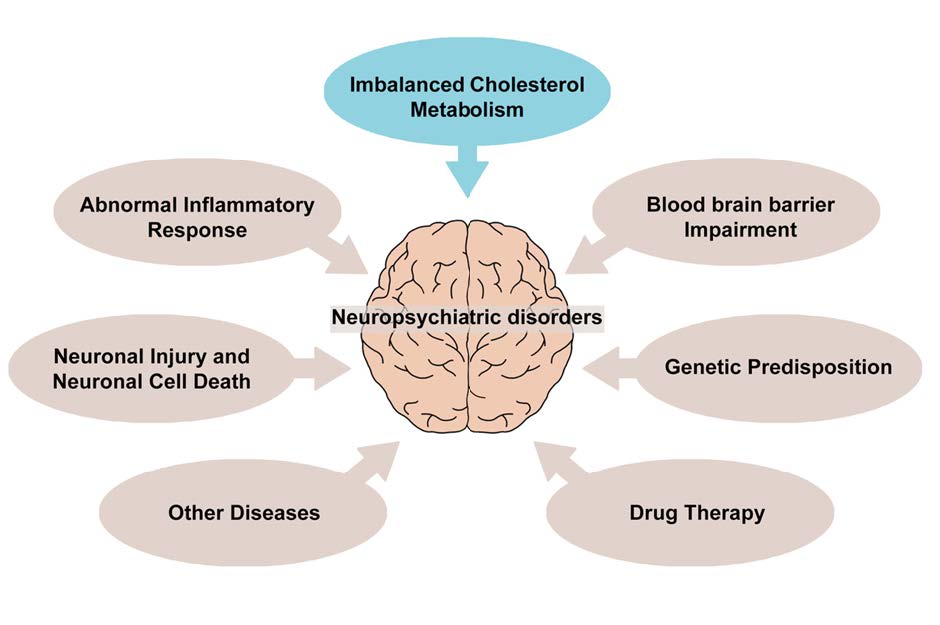
Keywords: Cholesterol, Major depressive disorders, Anxiety disorders, Neurons, Synapse, Neurotransmission


