Articles
Article Tools
Supplementary
Stats or Metrics
Article
Original Article
Exp Neurobiol 2023; 32(2): 68-82
Published online April 30, 2023
https://doi.org/10.5607/en23002
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
A Critical Involvement of Glutamatergic Neurons in the Anterior Insular Cortex for Subdiaphragmatic Vagotomy-induced Analgesia
Yea Jin Kim1, Grace J Lee1, Sang Wook Shim1, Doyun Kim2 and Seog Bae Oh1,2,3*
1Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, College of Natural Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080,
2Tooth-Periodontium Complex Medical Research Center, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080,
3Department of Neurobiology & Physiology, School of Dentistry and Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
TEL: 82-2-740-8656, FAX: 82-2-762-5107
e-mail: odolbae@snu.ac.kr
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
Subdiaphragmatic vagotomy (SDV) is known to produce analgesic effect in various pain conditions including not only visceral pain but also somatic pain. We aimed to determine brain mechanisms by which SDV induces analgesic effect in somatic pain condition by using formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain model. We identified brain regions that mediate SDV-induced analgesic effect on acute inflammatory pain by analyzing c-Fos expression in the whole brain. We found that c-Fos expression was specifically increased in the anterior insular cortex (aIC) among subregions of the insular cortex in acute inflammatory pain, which was reversed by SDV. These results were not mimicked in female mice, indicating sexual-dimorphism in SDV-induced analgesia. SDV decreased c-Fos expressions more preferentially in glutamatergic neurons rather than GABAergic neurons in the aIC, and pharmacological activation of glutamatergic neurons with NMDA in the aIC inhibited SDV-induced analgesic effect. Furthermore, chemogenetic activation of glutamatergic neurons in the aIC reversed SDV-induced analgesia. Taken together, our results suggest that the decrease in the neuronal activity of glutamatergic neurons in the aIC mediates SDV-induced analgesic effect, potentially serving as an important therapeutic target to treat inflammatory pain.
Graphical Abstract
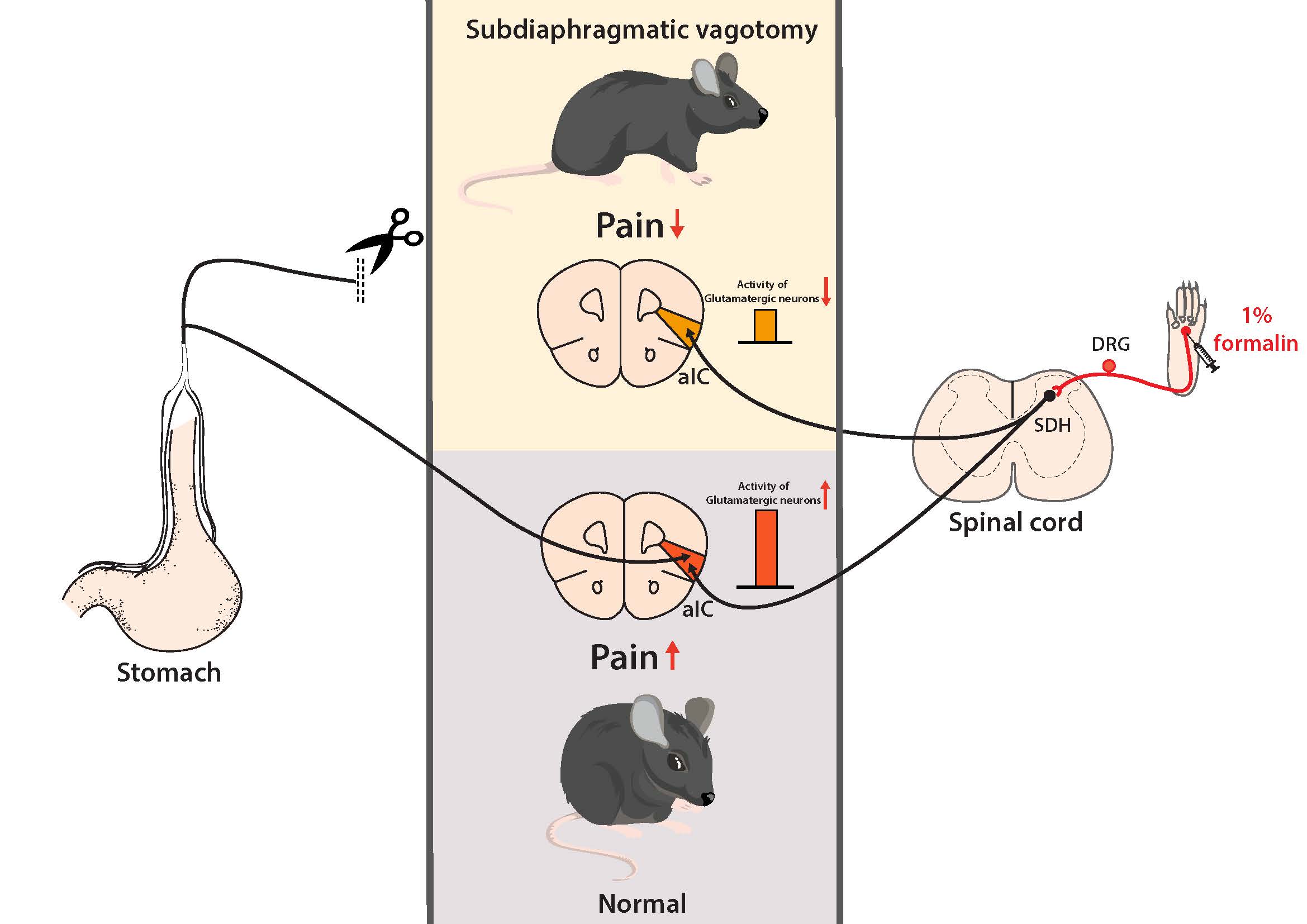
Keywords: Subdiaphragmatic vagotomy (SDV), Acute inflammatory pain, Anterior insular cortex, Glutamatergic neuron


