Articles
Article Tools
Stats or Metrics
Article
Original Article
Exp Neurobiol 2023; 32(6): 395-409
Published online December 31, 2023
https://doi.org/10.5607/en23039
© The Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences
Mapping Astrocytic and Neuronal μ-opioid Receptor Expression in Various Brain Regions Using MOR-mCherry Reporter Mouse
Woojin Won1†, Daeun Kim1,2†, Eunjin Shin1 and C. Justin Lee1*
1Center for Cognition and Sociality, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Daejeon 34126, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Information and Biotechnology, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), Ulsan 44919, Korea
Correspondence to: *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
TEL: 82-42-878-9150, FAX: 82-42-878-9151
e-mail: cjl@ibs.re.kr
†These authors contributed equally to this article.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
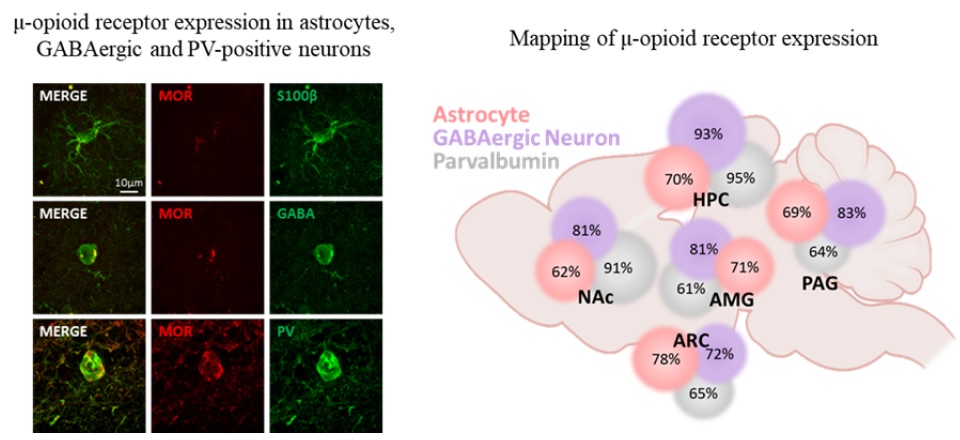
The μ-opioid receptor (MOR) is a class of opioid receptors characterized by a high affinity for β-endorphin and morphine. MOR is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that plays a role in reward and analgesic effects. While expression of MOR has been well established in neurons and microglia, astrocytic MOR expression has been less clear. Recently, we have reported that MOR is expressed in hippocampal astrocytes, and its activation has a critical role in the establishment of conditioned place preference. Despite this critical role, the expression and function of astrocytic MOR from other brain regions are still unknown. Here, we report that MOR is significantly expressed in astrocytes and GABAergic neurons from various brain regions including the hippocampus, nucleus accumbens, periaqueductal gray, amygdala, and arcuate nucleus. Using the MOR-mCherry reporter mice and Imaris analysis, we demonstrate that astrocytic MOR expression exceeded 60% in all tested regions. Also, we observed similar MOR expression of GABAergic neurons as shown in the previous distribution studies and it is noteworthy that MOR expression is particularly in parvalbumin (PV)-positive neurons. Furthermore, consistent with the normal MOR function observed in the MOR-mCherry mouse, our study also demonstrates intact MOR functionality in astrocytes through iGluSnFr-mediated glutamate imaging. Finally, we show the sex-difference in the expression pattern of MOR in PV-positive neurons, but not in the GABAergic neurons and astrocytes. Taken together, our findings highlight a substantial astrocytic MOR presence across various brain regions.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords: Astrocytes, Mu-opioid receptor, Mapping, Sex-difference


